The module Anamnesis and Clinical Diagnosis (incl. Basic Data Set) is used to accurately record known cardiovascular risk factors, previous diagnoses and interventions.
The collected findings enable a detailed assessment of a patient’s cardiovascular risk.
The module contains among others the mandatory basic data set with 42 items.
In the following, these items are labeled with **.
The examinations ought to be performed according to DZHK-SOP-K-02 .
The examinations ought to be performed according to DZHK-SOP-K-02 .
Content
- General information relating to the anamnesis
- Physical Examination and Sociodemographic Data
- Cardiovascular risk factors
- Cardiac Diagnoses (Anamnesis and Previous Findings)
- Previous cardiovascular interventions
- Current secondary diagnoses
- Anamnestic questions for women only
- Blood pressure after 5 minutes at rest
- Heart rate after sitting down for 5 minutes
- Further diagnoses
- Laboratory diagnostics (blood)
General information relating to the anamnesis
Date of examination**
is defined as the date on which the examination takes place. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_datum Data type: Timestamp with day, month and year
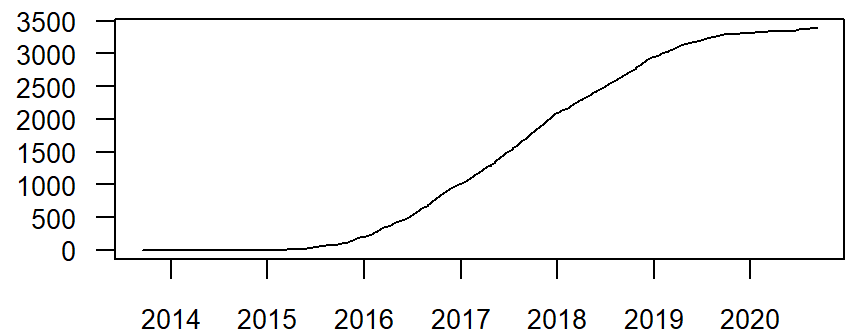
Figure: Number of records cumulatively by date of invastigation
Quality level
DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- Level 1: The examination is performed in accordance with the guidelines of the medical associations.
- Level 2: The examination is performed in accordance with the specifications of the DZHK SOP. Minimum requirements to ensure the quality of the implementation and the examiners are defined in the SOP.
- Level 3: The examination is performed in accordance with the specifications of the DZHK SOP and certification of the examiners: Definition of intr-observer and interobserver-variability (standard of epidemiological studies).
Fieldname: gehtest_qualitaet
Data type: Integer with following options
1
2
3
Physical Examination and Sociodemographic Data
Sex and date of birth**
are defined as the data which appear on the person’s identity card. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_geschlecht
Note in CRF: Sex
Data type: String with following options
male
female
unknown
not assessed
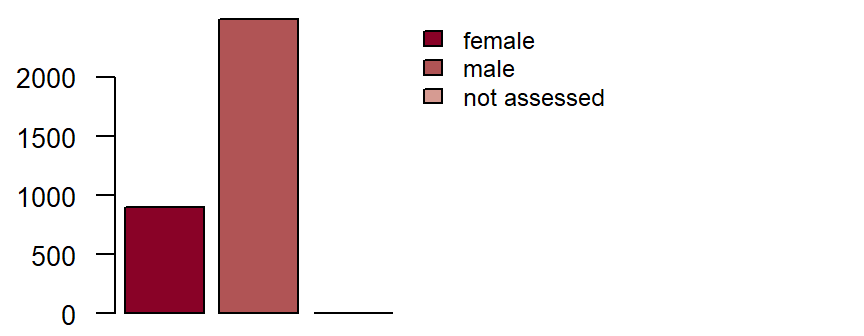
Figure: Number of records by sex
Fieldname: basis_gebdatum Note in CRF: Date of Birth Data type: Timestamp with month and year

Figure: Number of records by year of birth
Height and weight**
Height is measured in the standing position, without shoes and without head covering. Weight is measured in normal street clothing, without a jacket and without shoes. Preferentially, measured data should be collected; only when this is not possible (e.g. in the case of bed-ridden patients) should one estimate the values or resort to information provided by the proband. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_groesse Note in CRF: Height Data type: Integer with maximum 3 digits
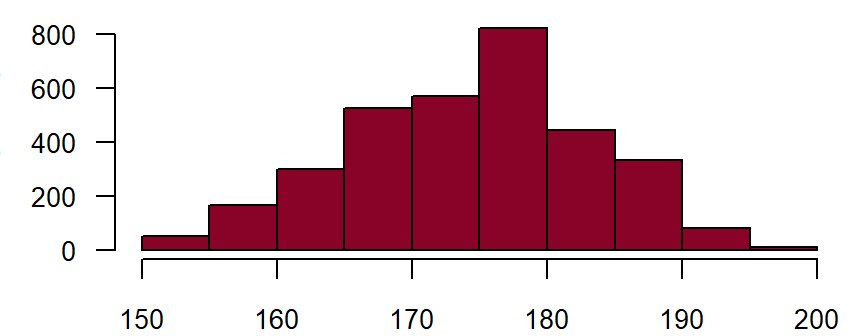
Figure: Number of records by height in centimetre
Fieldname: basis_gewicht Note in CRF: Weight Data type: Integer with maximum 3 digits

Figure: Number of records by weight in kilogram
Ethnicity**
A person’s ethnic origin is defined by their ancestry in relation to a specific ethnic group. This can be determined biologically and/or geographically on the basis of membership of a certain settlement group. Accordingly, a person’s skin colour can also be broadly defined. The colour spectrum can be differentiated from light to dark skin colour. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_ethnie
Note in CRF: Ethnicity: kaukasian
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by ethnicity
Family history of myocardial infarction or stroke**
is defined as a medically diagnosed myocardial infarction or stroke in one or both biological parents, biological siblings (including half-siblings) or biological children, provided the female relative was under age 65, or the male relative under age 55 (when the myocardial infarction/stroke occurred). DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_family
Note in CRF: Family history of myocardial infarction or stroke in parents, siblings or children under the age of 65 for women or under 55 for men
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unknown
not assessed
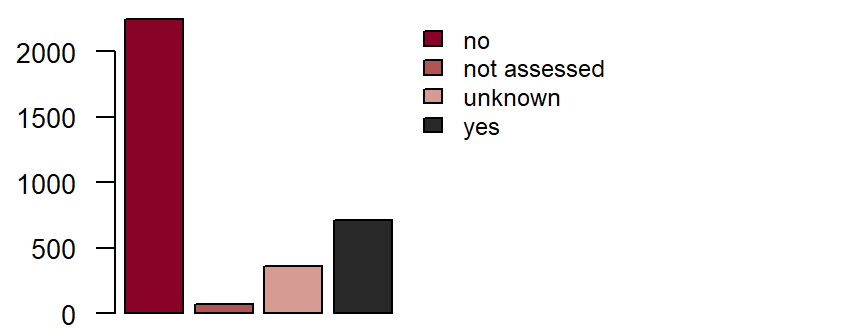
Figure: Number of records by family history of myocardial infarction or stroke
Cardiovascular risk factors
Diabetes mellitus**
is defined as diabetes which has been diagnosed and/or treated by a doctor. The American Diabetes Association criteria are:DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- haemoglobin A1c ≥ 6.5 % or a fasting blood glucose level of ≥ 126 mg/dl or a
- 2-hour blood glucose level of ≥ 200 mg/dl in the oral glucose tolerance test.
Fieldname: basis_diabetes
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by Diabetes mellitus
Arterial hypertension**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis of arterial hypertension which was diagnosed and/or is being treated by a doctor. Treatment can consist of e.g. dietary changes, physical activity and/or medication. Systolic blood pressure values ≥ 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure values ≥ 90mmHg measured by a doctor on at least two separate days after a 5-minute resting phase qualify for a diagnosis of arterial hypertension. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_hypertonie
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
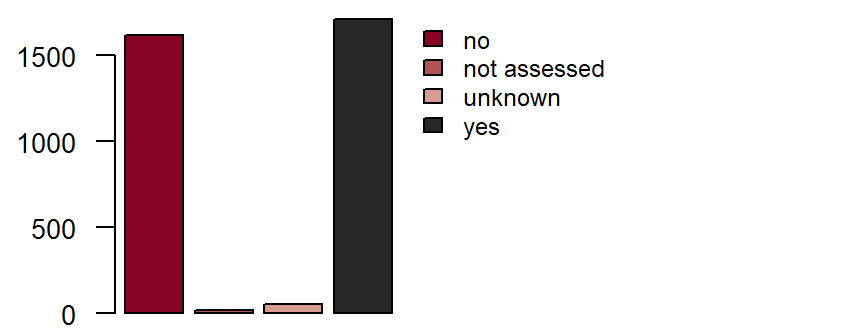
Figure: Number of records by arterial hypertension
Dyslipidaemia**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis of dyslipidaemia which was diagnosed and/or is being treated by a doctor. One or more of the following criteria:DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dl,
- LDL cholesterol ≥ 130 mg/dl,
- HDL cholesterol
< 40 mg/dl (men) and< 50 mg/dl (women).
Fieldname: basis_dyslipi
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
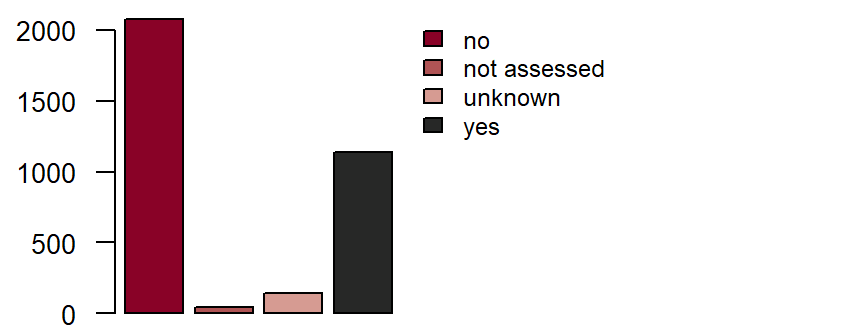
Figure: Number of records by dyslipidaemia
Smoker
Smoker**
is defined as current or previous use of cigarettes, cigars, pipes or smokeless tobacco.DZHK-SOP-K01: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- “Yes” for daily or occasional smoking (≥ 1x/month);
- “Ex-smoker“ for abstinence of more than 6 months; ex-smoker since …;
- “No“ for “never smoked“.
Fieldname: basis_raucher
Note in CRF: Smoker
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
ex-smoker (stopped ≥ 6 mth. ago)
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by smoker
Ex-Smoker**
Fieldname: basis_exrauch Note in CRF: Ex-smoker since Data type: Timestamp with year
Pack years
is the product of the number of years of cigarette smoking multiplied by the average number of packs smoked per day.
Example: A patient who has smoked 2 packets of cigarettes per day for 20 years has 40 pack years.
DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_packyear Data type: Integer with maximum 3 digits
Drinks per week
is the number of alcoholic drinks consumed per week. One drink is defined as e.g. 0.25 l of beer, 0.1 l of wine or 0.02 l of spirits.
Example: A patient who drinks 0.5 l beer on average two times every week has 4 drinks per week.
DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_drinksweek Date type: Integer with maximum 3 digits
Medically diagnosed alcoholism**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis of alcoholism which was diagnosed and/or is being treated by a doctor. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_alkoholkrank
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Renal failure
Renal failure
This includes all patients who exhibit reduced renal function. If known, the degree of renal dysfunction should be quantified by the estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR). Different estimation methods exist; if available, the formula that follows the MDRD formula should be used. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname:basis_niereinsuf
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Degree of renal dysfunction
Fieldname:basis_niereinsufgrad
Data type: String with following options
1 - GFR 90ml/min or higher
2 - GFR 60-89ml/min
3 - GFR 30-59ml/min
4 - GFR 15-29ml/min
5 GFR < 15ml/min or current dialysis dependency
unkown
not assessed
Current dialysis dependency**
is defined as current regular, at least weekly, renal replacement therapy (including haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis) within the last 30 days. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_dialyse
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by current dialysis dependency
Cardiac Diagnoses (Anamnesis and Previous Findings)
Coronary heart disease**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis by a doctor with one or more of the following criteria:DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- coronary artery stenosis of ≥ 50 % (diagnosed by cardiac catheterization or another direct coronary artery imaging method),
- prior coronary artery bypass operation,
- prior percutaneous coronary intervention,
- arteriosclerosis-induced myocardial infarction.
Fieldname: basis_khk
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by coronary heart disease
Status post myocardial infarction**
is a diagnosis of the disease by a doctor. Explanation: Acute myocardial infarction is defined as demonstrated evidence of myocardial necrosis in a clinical setting which is consistent with myocardial infarction. One or more of the following criteria must apply: Evidence of an increase or decrease of a cardiac biomarker (preferably troponin) with at least one value above the 99 % percentile of the upper reference limit and, additionally, at least one of the following factors:DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- symptoms of ischaemia, angina pectoris,
- ECG changes indicative of new ischaemia, e.g. ST segment elevations or a new left bundle branch block, development of pathological Q waves in the ECG,
- imaging studies show a loss of viable myocardial tissue or new regional wall motion abnormalities
- angiographic evidence of stenosis/blood vessel blockage.
Fieldname: basis_myokard
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by status post myocardial infarction
Cardiomyopathy**
is defined as a diagnosis by a doctor of a primary heart muscle disease. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
If the following question is answered with “yes”, please complete the Cardiomyopathy Diagnostics form.
Fieldname: basis_kardmyopath
Note in CRF:If the response to this question is “yes”, please complete the “Cardiomyopathy Diagnostics” form.
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by cardiomyopathy
Heart failure
Heart failure**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis and documentation by a doctor of heart failure, based on the following symptoms: shortness of breath with mild exertion, recurrent shortness of breath when sitting, fluid overload or pulmonary rales, distention of the neck veins, pulmonary oedema on physical examination or pulmonary oedema on chest x-rays. Documentation of reduced left ventricular function alone in the absence of clinical signs of heart failure does not meet the criteria for heart failure. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_insuffizienz
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by heart failure
S.p. decompensation
Status post decompensation is defined as any previous admission to a hospital with symptoms of heart failure (see above). DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzin_dekom
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Initial diagnosis of heart failure
Initial diagnosis of heart failure is defined as the time point when heart failure was diagnosed for the first time by a doctor. Hence it does not refer to the time point of first onset of symptoms, which is often much earlier. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzin_jahr Data type: Timestamp with year
Current NYHA class
Classification of the patient’s symptoms based on the New York Heart Association classification of heart failure:DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- NYHA I: No symptoms
- NYHA II: Symptoms with heavy physical exertion
- NYHA III: Symptoms with light physical exertion
- NYHA IV: Symptoms while at rest
Fieldname: basis_herzin_nyha
Data type: String with following options
I
II
III
IV
unkown
not assessed
Atrial fibrillation/flutter**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis by a doctor of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. It is defined as an episode of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter lasting at least 30 seconds or atrial fibrillation with evidence on the surface ECG or during pacemaker interrogation. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_vorhof
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by atrial fibrillation/flutter
Current or previous medical diagnosis of heart valve disease**
is defined as heart valve disease (incompetence or stenosis), which has been diagnosed and/or treated by a doctor. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzklap
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by heart valve disease
Diagnosis by a doctor of endocarditis
If at any time, currently or in their previous medical history, a patient has been diagnosed by a doctor with endocarditis (heart valve inflammation), it will be documented here. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_endo
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Diagnosis by a doctor of a congenital heart defect**
If a patient has a known congenital heart defect, it will be coded here. Congenital heart defects include shunt defects (e.g. ASD, VSD), congenital valvular heart diseases (e.g. pulmonary stenosis) and cardiomyopathies diagnosed in the first five years of life. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_ahf
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by congenital heart defect
Previous cardiovascular interventions
Interventional coronary revascularization
Interventional coronary revascularization**
is defined as a percutaneously performed intervention on a coronary artery, e.g. PTCA, stent implantation, rotablation et cetera. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_revas
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by revascularization
If yes, date of last intervention
Where applicable, the date of the last intervention should be entered. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_revas_date Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Peripheral revascularization
Peripheral revascularization
is defined as a percutaneously performed intervention on a peripheral artery (not including coronary arteries or bypass grafts) e.g. PTA, stent implantation, rotablation et cetera. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_perirevas
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
If yes, date of last intervention
Where applicable, the date of the most recent intervention should be entered.
DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_perirevasdate Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Coronary bypass operation
Coronary bypass operation**
is defined as operative myocardial revascularization by means of a bypass graft (e.g. from the internal thoracic artery or using arterial/venous grafts). Where applicable, the date of the most recent operation should be entered. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_bypass
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by coronary bypass operation
If yes, date of last intervention
Where applicable, the date of the most recent operation should be entered. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_bypass_date Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Other vascular operation
Other vascular operation
is defined as an operation of any kind on non-coronary blood vessels. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_gefaessop
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
If yes, date of last intervention
Where applicable, the date of the most recent operation should be entered. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_gefaessopdate Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Heart valve operation
Heart valve operation**
is defined as a minimally invasive percutaneous (catheter-based) or open surgical procedure on a heart valve. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzklap_op
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by heart valve operation
If yes, date of last intervention
Where applicable, the date of the most recent operation should be entered. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzklopdate Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Type of last intervention
The most recent event is to be coded according to type, whereby any transapical aortic valve replacements are to be coded as “catheter-based“. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzklopart
Data type: String with following options
open surgery
catheterbased
unkown
not assessed
If open surgery
In addition, details of the surgical procedure should be given. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_herzklopchir
Data type: String with following options
replacement
reconstruction
unkown
not assessed
If more than one procedure on one valve was performed, please provide details of the last Op (= current state)
Aortic valve
Fieldname: basis_aort
Data type: String with following options
native
reconstruction
mechanical prosthesis
bioprosthesis (open)
TAVI
unkown
not assessed
Fieldname: basis_taviauspraeg
Data type: String with following options
transfemoral
transapical
transaortal
unkown
not assessed
Pulmonic valve
Fieldname: basis_pulm
Data type: String with following options
native
reconstruction
mechanical prosthesis
bioprosthesis (open)
unkown
not assessed
Mitral valve
Fieldname: basis_mitral
Data type: String with following options
native
reconstruction
mechanical prosthesis
bioprosthesis (open)
clipping
unkown
not assessed
Triscuspid valve
Fieldname: basis_trik
Data type: String with following options
native
reconstruction
mechanical prosthesis
bioprosthesis (open)
unkown
not assessed
Implantable cardiac pacemaker or defibrillator
Implantable cardiac pacemaker or defibrillator**
is defined as status post implantation of a cardiac pacemaker or intracardiac defibrillator. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_schrittmacher
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
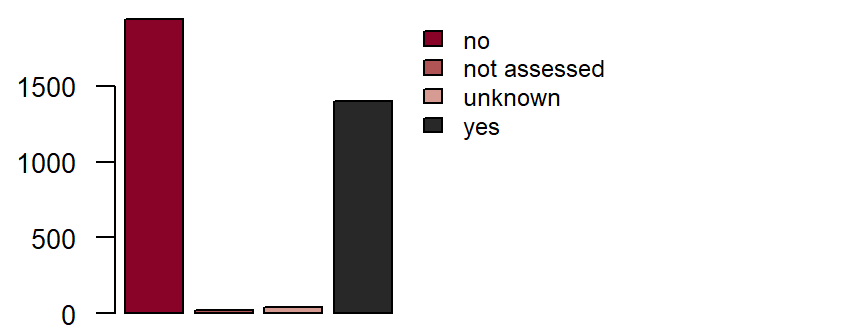
Figure: Number of records by pacemaker/defibrillator
If yes, what was implanted?
Fieldname: basis_schrittart
Data type: String with following options
pacemaker
defibrillator
unkown
not assessed
If yes, date of last event (implantation/exchange)
Where applicable, the date of the most recent operation (implantation/exchange) is to be entered. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_schrittdate Data type: Timestamp with month and year
If pacemaker, please give pacemaker type
In addition, the number of leads currently connected to the pacemaker power supply should be coded. A device with only one lead should be coded as a 1-chamber pacemaker, a device with an atrial and a ventricular lead should be coded as a 2-chamber pacemaker. Devices for cardiac resynchronization therapy, with 2 ventricular leads, should be coded as biventricular (CRT) pacemakers. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_schritttyp
Data type: String with following options
1-chamber-pacemaker (e.g. VVI)
2-chamber-pacemaker (e.g. DDD)
biventricular pacemaker (CRT)
unkown
not assessed
Other devices
are defined as other implantable devices for cardiac/vascular support. This includes devices for cardiac contractility modulation, for neuromodulation (e.g. vagus nerve stimulator, baroreceptor stimulator), intra-aortic balloon pumps and left ventricular cardiac assist devices. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Other devices
Fieldname: basis_schrittandere
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM)
Fieldname: basis_schrittccm
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)
Fieldname: basis_schrittiabp
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Other devices
Fieldname: basis_schrittsonst Data type: Free text
S.p. myocardial biopsy
S.p. myocardial biopsy
is defined as status post bioptic removal of tissue from the heart muscle (e.g. during a right/left catheter examination or operation). DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_biopsie
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Date of myocardial biopsy
Where applicable, the date of the most recent myocardial biopsy should be coded. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_biopsie_date Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Biopsy sites
Where applicable, the sampling site should be coded. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_biopsieentnahm
Data type: String with following options
left ventricle
right ventricle
left and right ventricle
unkown
not assessed
Current secondary diagnoses
PAOD
PAOD**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis by a doctor of peripheral arterial occlusive disease (in the blood vessels of the pelvis and legs, or from the upper extremity of the subclavian artery to the distal extremity). Renal, coronary, cerebral and mesenteric blood vessels and aneurysms are excluded. Possible symptoms are:DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- intermittent claudication,
- amputation due to severe arterial vascular insufficiency,
- vascular reconstruction, bypass operation or percutaneous revascularization,
- a positive non-invasive test (e.g. ankle-brachial index of ≤ 0.9, pathological TCPO2 measurement, evidence of 50 % or greater stenosis of a peripheral artery by Doppler/duplex sonography, CT, MRT, or angiography).
Fieldname: basis_pavk
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by PAOD
Fontaine stage
Classification of the degree of severity is done according to the Fontaine classification:
- Stage I: Asymptomatic PAOD
- Stage II: Intermittent claudication
- with walking distances > 200 metres (Stage IIa)
- with walking distances
< 200 metres (Stage IIb)- Stage III: Pain at rest
- Stage IV: Necrosis, gangrene
- trophic disorder, dry necroses (Stage IVa)
- bacterial infection of the necrosis, wet gangrene (Stage IVb)
DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_pavk_font
Data type: String with following options
I
IIa
IIb
III
IV
unkown
not assessed
Acute ischaemic occlusion
Acute ischaemic occlusion describes a recent (in the last 30 days) occurrence of demonstrated acute ischaemic occlusion of a peripheral arterial vessel. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_pavk_isch
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Stroke/TIA
Stroke/TIA**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis by a doctor. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_schlagtia
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by stroke/TIA
Date
Fieldname: basis_schlag_date Data type: Timestamp with month and year
Aetiology and Diagnosis
DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
- Ischaemic stroke: Infarction of tissue of the central nervous system, either symptomatic or silent (asymptomatic).
- Transient ischaemic attack (TIA): A transient episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain, spinal cord or retinal ischaemia without acute infarction which resolves completely within 24 hours. This definition is not met by chronic (non-vascular) neurological diseases or other acute neurological diseases such as metabolic or ischaemic encephalopathy resulting from general hypoxia (e.g. in the case of respiratory insufficiency, following a cardiac/circulatory arrest).
- Haemorrhagic stroke: Neurological dysfunction caused by intra-cranial bleeding.
- Stroke where there is uncertainty as to whether the cause was haemorrhagic or ischaemic.
Fieldname: basis_schlagaetiolog
Data type: String with following options
ischaemic
haemorrhagic
unkown
not assessed
Fieldname: basis_schlagdiag
Data type: String with following options
TIA
stroke
unkown
not assessed
Stroke severity
A stroke is described as “minor“ when the neurological symptoms can be completely reversed within 30 days or the change in the NIH Stroke Scale (see Appendix 7.3 NIH Stroke Scale) amounts to less than 3 points in comparison with the NIH Stroke Scale before the stroke. A stroke is described as “major” when a neurological deficit can still be demonstrated 30 days after the event or the NIH Stroke Scale is at least 3 points higher than prior to the stroke. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_schlagschwer
Data type: String with following options
minor
major
unkown
not assessed
Consequences of the stroke
A stroke is described as “disabling” when more than 2 points are scored on modified Rankin Scale 90 days after the stroke. If the modified Rankin Scale score is 2 points or less 90 days after the stroke, the stroke is described as “non-disabling”. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_schlagfolge
Data type: String with following options
disabling
non-disabling
unkown
not assessed
Chronic lung disease**
is defined as a diagnosis by a doctor of a chronic lung disease (e.g. COPD, chronic bronchitis, pulmonary fibrosis) and/or their pharmacological treatment, for example, with inhalable or oral pharmaceuticals. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_copd
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
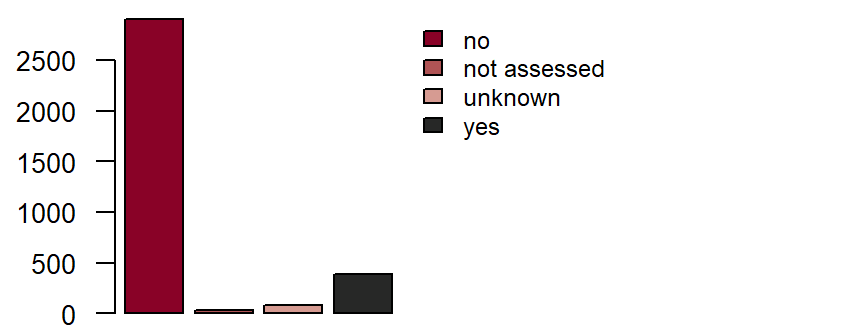
Figure: Number of records by chronic lung disease
Primary pulmonary hypertension
is defined as a diagnosis and/or treatment by a doctor of primary pulmonary hypertension. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_pulhyper
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Depression**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis by a doctor. The administration of antidepressants alone does not qualify for a diagnosis of depression. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_depression
Note in CRF: If the response to this question is “yes”, please complete the “Depression” form.
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by depression
Cancer more than 5 years ago**
is defined as a current or previous diagnosis of a malignant cancer. Basal cell carcinoma does not belong to malignancy. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_malignom
Note in CRF: Malignom
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by cancer(>5Y)
Cancer within the last 5 years**
Fieldname: basis_malignom_w5j
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by cancer(<5Y)
Anamnestic questions for women only
Menopause**
Fieldname: basis_meno
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed

Figure: Number of records by menopause
Year of Menopause**
Fieldname: basis_menojahr Data type: Timestamp with year
Day last menstrual period began**
Fieldname: basis_regeldat Data type: Timestamp with year, month and day
Blood pressure after 5 minutes at rest
Systolic**
The systolic blood pressure should be measured using a blood pressure monitor that is serviced and calibrated on a regular basis. Where possible, tested devices (e.g. Omron 705 IT) should be used for epidemiological trials. Blood pressure measurement begins after the patient has been at rest for at least 5 minutes. Three readings are taken at intervals of 2 minutes; the average values of the second and third readings are entered into the CRF. DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_systol Note in CRF: Systolic Data type: Integer with maximum 3 digits
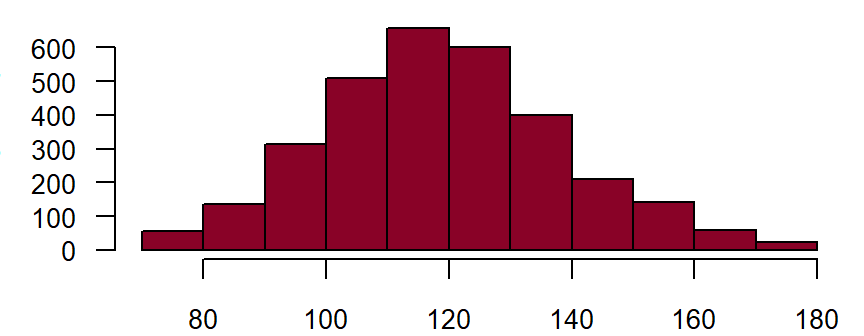
Figure: Number of records by systolic blood pressure in mm Hg
Diastolic**
Feldname: basis_diastol Note in CRF: Diastolic Data type: Integer with maximum 3 digits
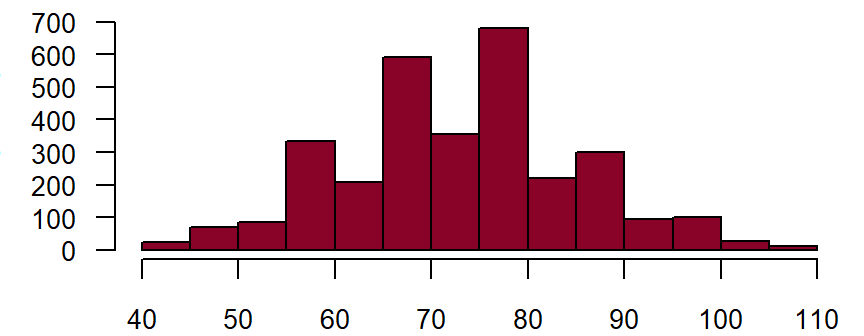
Figure: Number of records by diastolic blood pressure in mm Hg
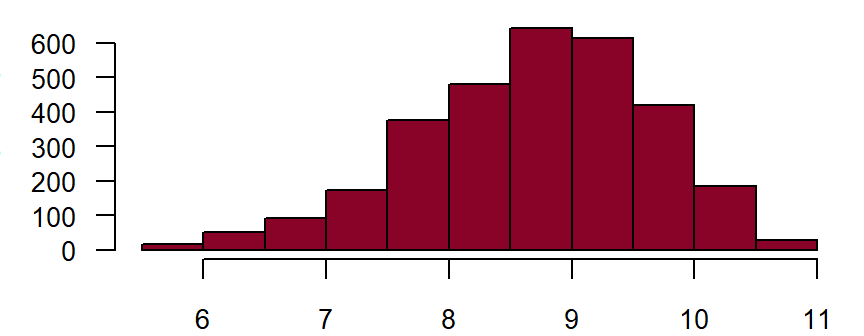
Heart rate after sitting down for 5 minutes **
Measurement of the heart rate begins after the patient has been sitting down for at least 5 minutes. This should take place after measuring the blood pressure. This should be done manually by counting the radial pulse for 30 seconds; that value multiplied by two should be entered into the CRF (beats/minute). DZHK-SOP-K02: Basic data set - Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses/Physical Examination, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_frequenz Note in CRF: Heart rate Data type: Integer with maximum 3 digits
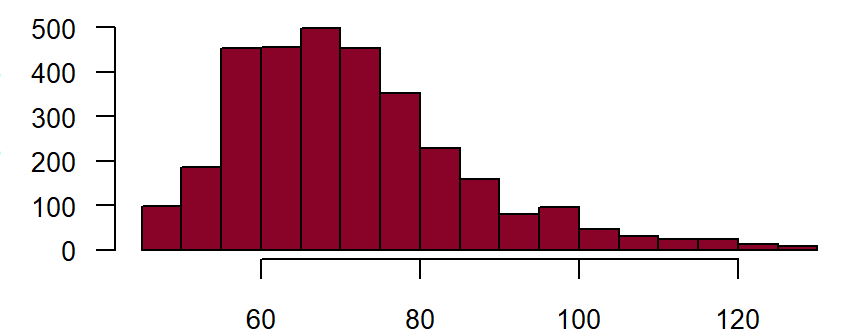
Figure: Number of records by heart rate
Further diagnoses
Dyspnoea on exertion
A patient who complains of shortness of breath with physical exertion within the last 14 days and/or at present. In cases of known heart failure, for patients in NYHA stages II-IV, dyspnoea on exertion should be coded. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_bdyspnoe
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Dyspnoea at rest
A patient who complains of shortness of breath even when at rest (e.g. when talking) within the last 14 days and/or aatpresent. In cases of known heart failure, for patients in NYHA stage IV, dyspnoea at rest should be coded. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_rdyspnoe
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Peripheral oedema
A patient who complains of bilateral accumulation of fluid in the extremities within the last 14 days and/or at present, whether clinically observed or perceived by the patient. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_oedeme1
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Jugular venous distention
The diagnostic test for jugular venous distention is conducted with the upper body of the patient positioned at a 45° angle. The level at which the jugular vein collapses is then determined. A non-pathological finding is if the vein collapses at latest at the level of the supra-sternal notch, which normally corresponds to an 8 cm water column or 5-6 mmHg before the right atrium. If the jugular vein collapses above the supra-sternal notch, jugular venous distention must be coded. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_halsvene
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Pulmonary rales
are defined as sounds heard over the lung during auscultation which are created by the movement of fluids and/or secretions during inspiration and expiration. They belong to the category of adventitious breath sounds overlying normal breath sounds and indicate a pathological change in the lung. DZHK-SOP-K-02: Anamnesis/Clinical Diagnoses, Version: V1.0, Valid as of: 01.09.2014
Fieldname: basis_pulmo
Data type: String with following options
yes
no
unkown
not assessed
Laboratory diagnostics (blood)
Note in CRF: For clinically stable patients, not more than 1 week old, otherwise up to date!
Date of blood sample was taken**
Fieldname: basis_datum_blut Note in CRF: Where applicable, give date for the oldest value. Data type: Timestamp with year, month and day
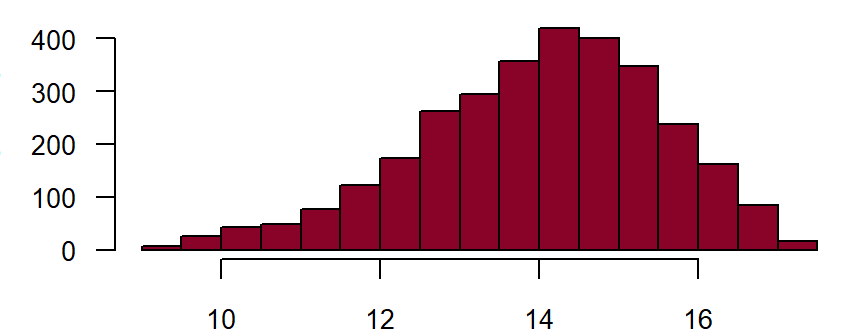
Haemoglobin**
Fieldname: basis_haemo Data type: Floating point number with 2 places before and 2 places after comma
Figure: Number of records by haemoglobin
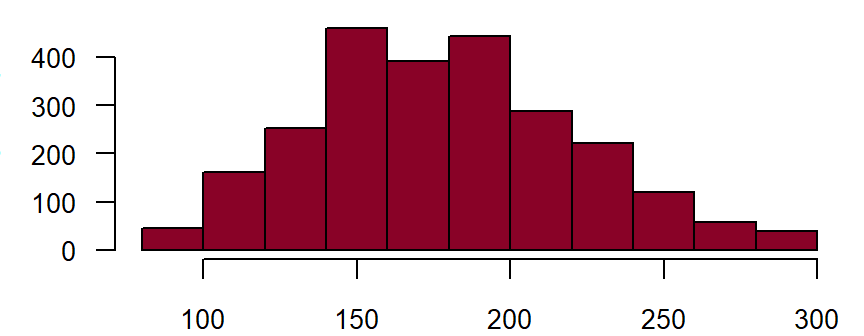
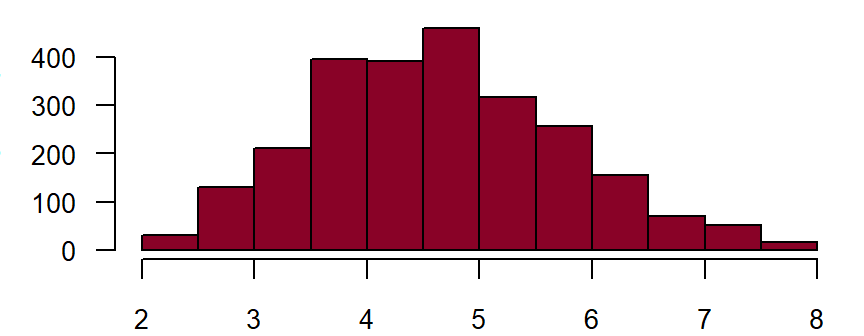
Creatinine (serum, heparin plasma)**
Fieldname: basis_kreatinin Data type: Floating point number with 4 places before and 3 places after comma
Figure: Number of records by creatinine